Twin-Tub Semi-Automatic Washing Machine Mold
The double-barrel semi-automatic washing machine mold is a high-precis...

Before detailed engineering begins, a clear understanding of the application and performance targets of a Plastic Sorting Box Mold is essential. Sorting boxes are typically used in logistics, manufacturing, and storage systems, where dimensional accuracy and repeatability are critical.
The overall size, wall thickness distribution, rib structure, and load-bearing areas determine how molten plastic flows and cools inside the cavity. Boxes designed for heavy-duty use usually require thicker sections, which directly influence runner size and cooling layout.
Common materials such as PP or HDPE have different flow lengths, shrinkage ratios, and cooling characteristics. Understanding these properties allows designers to predict deformation risks and compensate through mold structure.
Expected annual output and cycle time targets guide decisions such as single-cavity versus multi-cavity layouts and the complexity of the cooling system. High-volume production emphasizes stability and short cycles.
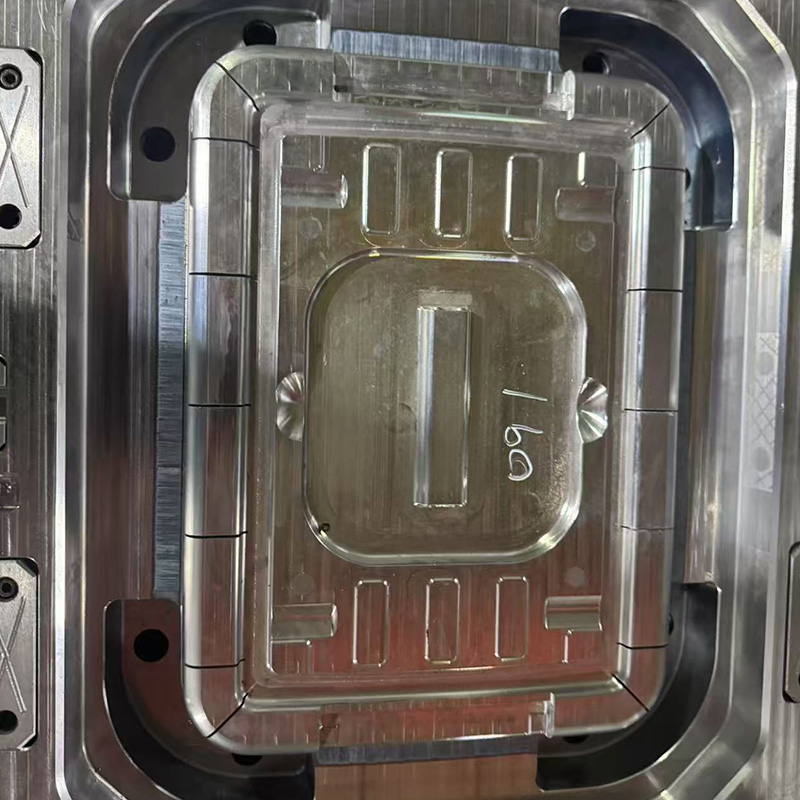
The runner system is responsible for delivering molten material from the injection machine nozzle to the cavity with pressure loss and temperature drop.
Full-round runners offer lowe flow resistance and thermal efficiency, while trapezoidal runners are often chosen for easier machining and maintenance. The choice depends on mold size and cost considerations.
For molds with multiple cavities or large surface areas, balanced runners ensure simultaneous filling. This prevents uneven shrinkage and reduces internal stress differences between parts.
Runner diameter must be carefully calculated based on shot volume, material viscosity, and injection speed. Undersized runners may cause short shots, while oversized runners increase material waste and cycle time.
Gate design directly affects filling behavior, surface appearance, and mechanical performance of the sorting box.
Fan gates and edge gates are widely used because they allow a wide melt entry, reducing shear stress and weld lines. These gate types are suitable for large, flat surfaces common in sorting boxes.
Placing the gate near thicker sections helps compensate for shrinkage and improves packing efficiency. Non-visible or non-functional areas are preferred to maintain clean external surfaces.
Gate thickness is usually slightly smaller than the part wall thickness to ensure smooth separation during ejection. Proper sizing also prevents excessive gate marks and stress concentration.
Cooling efficiency is one of the most critical factors affecting cycle time and product quality in a Plastic Sorting Box Mold.
Cooling channels should follow the contour of the cavity and be placed as close as possible to the molded surface without compromising mold strength. Uniform distance ensures even heat removal.
Thick areas such as bottom panels, ribs, and corners often require separate cooling circuits. Independent control helps prevent localized hot spots that cause warpage or sink marks.
For complex designs, baffles, bubblers, or conformal cooling inserts can significantly improve heat transfer efficiency. These solutions are especially useful for deep ribs and reinforced edges.
Successful mold performance depends on the integration of all three systems rather than optimizing each one independently.
Gate regions experience higher temperatures due to continuous melt flow. Additional cooling around these zones prevents material degradation and uneven shrinkage.
Proper vent placement works together with gate design to release trapped air during filling. This reduces burn marks and improves surface quality.
Fast filling must be matched with sufficient cooling before ejection. Balanced system design reduces deformation during demolding and improves production consistency.
Even a well-designed mold requires validation through real production trials.
Trials reveal potential issues such as flow hesitation, incomplete filling, or uneven cooling. Data collected during this stage guides further optimization.
Adjustments to runner dimensions, gate size, or coolant flow rates are often made to achieve a suitable balance between quality and efficiency.
Continuous monitoring during mass production ensures the mold maintains stable output and consistent quality over its service life.
Through systematic design and integration of runner, gate, and cooling systems, manufacturers can achieve reliable, efficient, and high-quality production of plastic sorting boxes that meet demanding industrial requirements.